Red5 Pro File Authentication Validator
ABOUT
The Red5 Pro File Authentication Validator is the one of the default validators provided with the simple auth plugin. It uses a simple filesystem-based datastore to validate credentials.
The validator expects the default location of the file to be {RED5_HOME}/conf/simple-auth-plugin.credentials. However, a different file can also be specified using the validator’s configuration options as long as the format is same.
This validator is best suited when only application connection level security is required and there is no need to handle publishers and subscribers separately.
MECHANISM
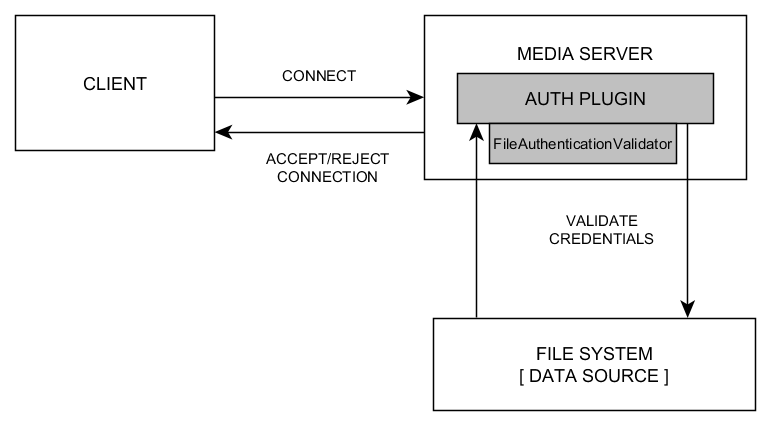
As the application starts up, the validator loads the .credentials file into memory and creates an internal data structure to store the username-password combinations for quick look up.
When a client attempts to connect to the application, it must provide the username and password parameters during the connection attempt. The simple auth checks to see if the parameters have been provided or not. If one or more parameters are missing the client is immediately rejected.
If credentials are provided, the validator checks to see if the username and password combination is present in its internal data structure. If the combination is found, the client is accepted -else it is rejected.
PREREQUISITES FOR SETTING UP AUTHENTICATION
CONFIGURING CREDENTIALS
The authentication module stores its credentials in the RED5_HOME/conf/simple-auth-plugin.credentials file unless you specify a custom location for the .credentials file. Each credential is stored as a property-value pair and all the credentials are loaded into memory when the server starts. If your scope configuration overrides this to use a different credentials file, the process to edit credentials would be the same as shown below.
A credential (username and password) pair is stored in a new line with a single space separating the username and the password.
Sample simple-auth-plugin.credentials file
#Simple auth credentials file
#[ Add username and password as key-value pair separated by a space (one per line) ]
#Example: testuser testpass
testuser testpassAdd a new entry by adding the new credentials in a new line.
#Simple auth credentials file
#[ Add username and password as key-value pair separated by a space (one per line) ]
#Example: testuser testpass
testuser testpass
newuser newpassRemove credentials by removing the line.
#Simple auth credentials file
#[ Add username and password as key-value pair separated by a space (one per line) ]
#Example: testuser testpass
newuser newpassNOTE: Red5 Pro server must be restarted for changes to take effect.
ENABLING SECURITY ON YOUR WEBAPP
To enable security on your web application, you need to add & configure the Simple Auth Plugin security bean along with the validator bean to your web application’s context file – red5-web.xml as explained below.
APPLICATION LEVEL CONFIGURATION
To attach simple auth plugin to a webapp using the Red5ProFileAuthenticationValidator validator, you need to specify the core plugin configuration bean along with the validator bean to use for authentication, in the application’s context (red5-web.xml) file.
Example 1: Attaching plugin security to the live webapp using Red5ProFileAuthenticationValidator for authentication with default configuration settings.
To apply security to the live application, you can add the security configuration to RED5_HOME/webapps/live/WEB-INF/red5-web.xml as shown below :
<bean id="simpleAuthSecurity" class="com.red5pro.server.plugin.simpleauth.Configuration" >
<property name="active" value="true" />
<property name="rtmp" value="true" />
<property name="rtsp" value="true" />
<property name="rtc" value="true" />
<property name="rtmpAllowQueryParamsEnabled" value="true" />
<property name="allowedRtmpAgents" value="*" />
</bean>The name of the bean must be simpleAuthSecurity, and it must instantiate the simple auth module configuration class – com.red5pro.server.plugin.simpleauth.Configuration.
With the following configuration applied, the application requests the plugin to force authentication on RTMP, RTSP and WebRTC connections. Also, the application requests the plugin to allow query string authentication for RTMP clients.
Example 2: Attaching plugin security to the live webapp using Red5ProFileAuthenticationValidator for authentication with custom configuration settings.
To specify a custom properties file as a data source for Red5ProFileAuthenticationValidator component, you can use the following configuration.
<bean id="authDataValidator" class="com.red5pro.server.plugin.simpleauth.datasource.impl.Red5ProFileAuthenticationValidator" init-method="initialize">
<property name="context" ref="web.context" />
<property name="dataSource" value="/WEB-INF/simple-auth-plugin.credentials" />
</bean>
<bean id="simpleAuthSecurity" class="com.red5pro.server.plugin.simpleauth.Configuration" >
<property name="active" value="true" />
<property name="rtmp" value="true" />
<property name="rtsp" value="true" />
<property name="rtc" value="true" />
<property name="rtmpAllowQueryParamsEnabled" value="true" />
<property name="allowedRtmpAgents" value="*" />
<property name="validator" ref="authDataValidator" />
</bean>In the above configuration, we instantiate the Red5ProFileAuthenticationValidator class with the context and relative path to the properties file. In this case, the authentication provider will use your validator instead of the default one and validate credentials against the information stored in your webapp’s WEB-INF/simple-auth-plugin.credentials.
__You can copy the file simple-auth-plugin.credentials from RED5_HOME/conf directory to your webapp’s WEB-INF directory.__
NOTE: IF ANY APPLICATION LEVEL PROPERTY IS MISSING IN YOUR CONFIGURATION BEAN DEFINITION, THE VALUE FOR THAT PROPERTY IS COPIED OVER FROM THE MASTER CONFIGURATION (PLUGIN CONFIGURATION).
APPLICATION LEVEL CONFIGURATION BEAN PROPERTIES
Following parameters are allowed in a bean configuration at the application level (configured in application’s red5-web.xml).
CORE
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| active | Boolean | Sets the state of security for the application |
| rtmp | Boolean | Sets the state of RTMP security for the application |
| rtsp | Boolean | Sets the state of RTSP security for the application |
| rtc | Boolean | Sets the state of WebRTC security for the application |
| rtmpAllowQueryParamsEnabled | Boolean | Sets the state of query string based authentication for RTMP clients |
| allowedRtmpAgents | String | Sets the list of allowed RTMP agent strings separated by semicolons. By default, all agent strings are allowed. |
| validator | Reference | Sets the reference to the validator bean to use for authentication |
VALIDATOR
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| context | Reference | The reference to the web.context bean |
| dataSource | String | Sets the path of the .credentials properties file relative to the webapp’s directory |
CLIENT AUTHENTICATION
RTMP, RTSP and WebRTC clients must provide connection parameters when attempting to establish a connection with the server. The plugin will extract two parameters (username and password) and try to match them against the username-password pairs in the properties file.
Given below are some snippets, explaining how authentication can be achieved for different client types.
Authenticating RTMP Clients
RTMP clients must pass authentication parameters (username and password) using the connection arguments in [NetConnection.connect](https://help.adobe.com/en_US/FlashPlatform/reference/actionscript/3/flash/net/NetConnection.html#connect())
Example A
var nc:NetConnection = new NetConnection();
nc.addEventListener(NetStatusEvent.NET_STATUS, onStatus);
nc.connect("rtmp://localhost/myapp", "testuser", "testpass");
function onStatus(ns:NetStatusEvent):void
{
trace(ns.info.code);
}Username and password should be the first two parameters in the arguments array being sent to Red5 Pro.
With the simpleauth.default.rtmp.queryparams=true in the plugin configuration file or using the rtmpAllowQueryParamsEnabled property of configuration bean set to true, RTMP clients can also pass parameters in the query string.
Example B
var nc:NetConnection = new NetConnection();
nc.addEventListener(NetStatusEvent.NET_STATUS, onStatus);
nc.connect("rtmp://localhost/myapp?username=testuser&password=testpass");
function onStatus(ns:NetStatusEvent):void
{
trace(ns.info.code);
}Authenticating RTSP Clients
RTSP clients (Android and IOS) must pass authentication parameters (username and password) using the R5Configuration object in the Red5 Pro Mobile SDK.
Android Example
R5Configuration config = new R5Configuration(R5StreamProtocol.RTSP,
TestContent.GetPropertyString("host"),
TestContent.GetPropertyInt("port"),
TestContent.GetPropertyString("context"),
TestContent.GetPropertyFloat("buffer_time"));
config.setParameters("username=testuser;password=testpass;");
R5Connection connection = new R5Connection(config);IOS Example
Swift
func getConfig()->R5Configuration{
// Set up the configuration
let config = R5Configuration()
config.host = Testbed.getParameter("host") as! String
config.port = Int32(Testbed.getParameter("port") as! Int)
config.contextName = Testbed.getParameter("context") as! String
config.parameters = @"username=testuser;password=testpass;";
config.`protocol` = 1;
config.buffer_time = Testbed.getParameter("buffer_time") as! Float
return config
}Authenticating WebRTC Clients
WebRTC clients (Using Red5pro HTML5 sdk) must pass authentication parameters using the connectionParams property of the baseConfiguration object.
Example:
var baseConfiguration = {
host: window.targetHost,
app: 'myapp',
iceServers: iceServers,
bandwidth: desiredBandwidth,
connectionParams: {username: "testuser", password: "testpass"}
};USE CASES
EFFECTIVE USE CASE SCENARIOS
- When you have users holding an account on your business server.
- When you need to know who is using your app (hence the username/password parameters).
- Two-way chat applications where both users will have a pair of credentials.
INEFFECTIVE USE CASE SCENARIOS
- When you need anonymous usage of your application (no fixed credentials for users).
- One to many applications (one broadcaster => N subscribers), where you need to distinguish between publishers and subscribers.