Ultra-low latency makes live video feel immediate. When delay drops below one second, conversations flow naturally, bids land fairly, and interactive experiences finally work as intended. In this guide, we explain what ultra-low latency streaming really means, why it matters, and how teams achieve sub-second delivery in production systems. Short on time? Skip to the… Continue reading What Is Ultra-Low Latency Streaming? Use Cases and Real-Time Delivery
Ultra-low latency makes live video feel immediate. When delay drops below one second, conversations flow naturally, bids land fairly, and interactive experiences finally work as intended. In this guide, we explain what ultra-low latency streaming really means, why it matters, and how teams achieve sub-second delivery in production systems.
Short on time? Skip to the section explaining how to achieve ultra-low latency in your streaming workflow.
Table of Contents
Latency Levels in Video Streaming
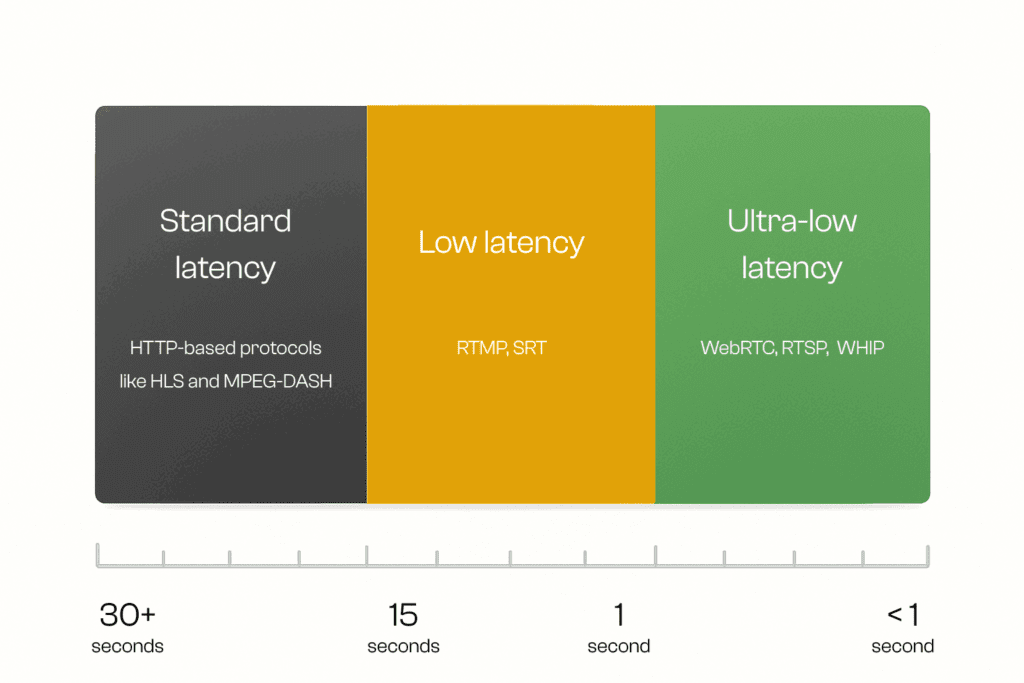
Three most common latency types.
Latency is the delay between when data is sent and when it is received. In streaming, this delay applies to both video and audio signals, affecting how natural and uninterrupted a live experience feels. Latency is introduced at multiple points: video and audio encoding, packet transmission across the network, buffering, and decoding on the playback device.
A related concept is latency jitter, which refers to fluctuations in that delay. Instead of a steady, predictable latency, the delay can vary from moment to moment, causing video to freeze, audio to skip, or streams to drift out of sync.
There are three main types of latency in streaming, each serving different use cases and protocols:
- Standard latency – Typically 15–30 seconds, common in HTTP-based protocols like HLS and MPEG-DASH, suitable for large-scale content delivery.
- Low latency – Around 3–10 seconds, achieved with optimizations such as Low-Latency RTMP and SRT, often used for sports, live events, and news.
- Ultra-low latency – Under 1 second, achieved with WebRTC and similar real-time protocols, designed for interactive applications like video conferencing, auctions, and online gaming.
What is Ultra-Low Latency Streaming?

Ultra-low latency streaming technology powers various real-time applications.
Ultra-low latency streaming is a technology that minimizes the delay between a live event happening and the moment it reaches viewers, reducing that gap to just milliseconds. In practice, ultra-low latency means end-to-end video delivery under one second, typically in the 200–400 millisecond range. It makes video delivery fast enough to support real-time interactivity, where conversations, actions, and reactions flow naturally without waiting for the stream to catch up.
In practice, ultra-low latency means more than cutting wait times. It is the foundation that enables next-generation applications such as live auctions, multiplayer gaming, drone operations, video conferencing, online betting, and emergency response. In these scenarios, even one second of delay can break immersion, cause financial loss, or create safety risks.
Some platforms label 1–4 seconds as ultra-low latency, but for interactive use cases, anything above one second still introduces noticeable delay. Ultra-low latency streaming technology we provide in Red5 Pro and Red5 Cloud achieves sub-250ms or ¼ second delivery, which is what many in the market now call real-time streaming. For simplicity in this post, we use the terms “ultra low latency” and “real-time latency” interchangeably.
The lowest latency achievable today for video streaming is typically around 200–400ms with WebRTC. At this level, interactive experiences feel seamless, and businesses can offer users the immediacy they expect from live video.
Why Is Ultra-Low Latency Streaming Needed?
Ultra-low latency streaming is essential because it ensures live video feels immediate, interactive, and secure. For both businesses and viewers, reducing delay to sub-second levels creates stronger engagement, prevents spoilers, and protects valuable content and revenue.
- Deliver live events as they happen. Keep concerts, sports, and broadcasts truly live so audiences feel connected to the action in real time without disruptive delays.
- Protect revenue opportunities. High latency leads to poor user experiences and billions in lost revenue across the video industry. Ultra-low latency streaming allows businesses to unlock new use cases and maximize monetization potential. For a deeper look at the financial impact, download our free whitepaper “The True Cost of Video Latency.”
- Enable natural interaction. Support smooth conversations in video calls, interviews, and news reporting by removing the awkward pauses caused by lag.
- Power interactive applications. Make real-time bidding in auctions, multiplayer gaming, live trivia, and betting fair and engaging by synchronizing responses.
- Improve reaction speed. Ensure drones, emergency response systems, and public safety teams receive video and audio instantly so they can act without hesitation.
- Boost audience engagement. Viewers stay longer on platforms that stream with minimal delay, driving loyalty and higher watch times for businesses.
- Secure live streaming content. Support advanced protections like DRM with forensic watermarking to fight piracy. By combining watermarking with real-time streaming under broadcast-level latency, distributors can identify and disrupt illegal streams quickly without sacrificing user experience.
- Meet user expectations. Audiences expect video to match the speed of messaging apps and social platforms. Sub-second latency helps retain viewers who demand immediacy.
The financial impact of achieving this level of performance is significant. As explored in our free whitepaper ‘The True Cost of Video Latency’, high latency not only causes poor user experiences but also translates into billions in lost revenue opportunities across the industry.
Elements Of Ultra-Low Latency Networks
Building an ultra-low latency streaming system requires more than just fast internet connections. It depends on a carefully designed infrastructure that minimizes every possible source of delay. The key elements include:
- Live streaming infrastructure. Scalable hardware and software supporting thousands or even millions of concurrent viewers requires a cross-cloud or multi-cloud design. This ensures that scaling up doesn’t add bottlenecks that increase delay.
- Codec. Video and audio must be compressed and decompressed quickly without sacrificing quality. Lightweight codecs like H.264, H.265,VP8, VP9, AV1, Opus and hardware acceleration with solutions from Amino, Oracle, Osprey Video, and Videon are often used to speed up this process.
- Efficient transport protocols. Traditional protocols like HLS introduce long delays due to buffering and chunked requests. Ultra-low latency networks rely on real-time protocols such as WebRTC or SRT that transmit data in smaller chunks and deliver them immediately.
- Edge computing. Placing processing power closer to the user reduces the physical distance data must travel. By using distributed edge servers, content can be delivered with far lower round-trip times.
Learn what causes latency and how to fix it in this blog.
How Ultra-Low Latency Is Achieved in Real Systems
Achieving ultra-low latency streaming requires removing delays at every stage of the video delivery pipeline. From capture and encoding to transport and playback, each component must be optimized to minimize buffering, reduce processing time, and shorten the physical distance data has to travel.
At a general level, ultra-low latency is achieved by:
- Using real-time transport protocols. Technologies such as WebRTC, SRT, and RTSP are designed to deliver video in milliseconds rather than seconds, unlike traditional methods such as HLS.
- Optimizing encoding and decoding. Lightweight codecs like H.264, H.265,VP8, VP9, AV1, Opus and hardware acceleration with solutions from Amino, Oracle, Osprey Video, and Videon help compress and decompress video quickly without adding noticeable delay.
- Deploying edge servers. Positioning servers closer to viewers reduces the distance content must travel, keeping delivery times sub-second.
- Adaptive bitrate streaming. Streams dynamically adjust to changing bandwidth conditions, preventing buffering interruptions.
- Intelligent routing. Networks choose the fastest available path for data to avoid congestion and minimize round-trip times.
For a deeper look at protocol-level strategies, see our articles 7 Ways WebRTC Solves Ultra-Low Latency Streaming and Keys to Optimizing End-to-End Latency with WebRTC.
How Red5 Approaches Ultra-Low Latency
At Red5, we focus on delivering real-time performance with our custom-built media server and Experience Delivery Network (XDN) architecture. This solution is optimized for speed and efficiency. By leveraging WebRTC along with other protocols like SRT, Zixi, and RTSP, Red5 Pro and Red5 Cloud regularly achieve video delivery under a quarter of a second.
The XDN architecture distributes streams from origin servers to strategically placed edge nodes, ensuring that each viewer is connected to the closest possible point. This reduces latency, balances traffic loads, and supports massive scalability for events with thousands or millions of participants. Customers can deploy XDN in the cloud, on-premises, or at the edge with providers such as AWS Wavelength, depending on their needs.
We also provide SDKs and APIs that make it simple for developers to integrate sub-second video into mobile apps or web platforms. As part of our approach, we partner with hardware providers and build custom integrations to get as close as possible to zero latency streaming. Read this study to learn about real-time streaming with Amino’s media players, visit this blog to see how to configure Videon’s encoder with Red5, or read this article to set up 4K streaming with Osprey Video encoder.
Use Cases For Ultra-Low Latency Streaming
It is crucial for a wide range of applications and industries. Here are just a few examples:
- Remote Production Workflows: Manage multiple contribution feeds on-premise and push them to the cloud for collaborative production.
- Live Sports Streaming: High latency breaks the experience. Fans expect real time at the venue or at home, and as watch parties and other interactive features grow, sub-second video becomes essential.
- Live Sports Betting: Bets must be placed and processed on current information. Even small delays cause missed opportunities or unfair advantages.
- GovTech: Sub-second streaming for traffic monitoring and smart cities, secure air-gapped video streaming and real-time drone feeds for public safety and defense.
- Surveillance and Security: Sub-second streaming enables real time monitoring and faster response to breaches or suspicious activity.
- News Broadcasting: Breaking updates need real time delivery so anchors, reporters, and viewers stay in sync and avoid talk-over.
- Online Auctions and Bidding: Sub-second latency keeps bids synchronized for all, increasing participation and final sale values.
- Online Casinos and Gambling: Live dealer and in-play wagers depend on real time video and data to maintain integrity and engagement.
- House of Worship Streaming: Broadcast religious services to remote congregations with secure, real-time video.
Real Examples Of Ultra-Low Latency For Live Streaming
Below are four real deployments that reached sub-250 ms experiences with Red5, plus the business results they unlocked.
Caltrans • Statewide Traffic Monitoring
Watch the Caltrans traffic monitoring demo on Youtube.
Caltrans aggregates video from thousands of highway cameras into a secure cloud where Red5 Pro and Nomad Media deliver real-time access for transportation, state, and law enforcement teams. Authorized users see live feeds instantly, review the last three days of footage, and rely on automated plate and face redaction for privacy. Real-time incident detection speeds decisions during accidents, congestion, and wildfire events, improving everyday operations and emergency response.
TorkHub • Multi-View Motorsports for Formula Drift

Real-Time Motorsports Streaming Application.
TorkHub built a synchronized racing experience with Red5 Pro, combining live multi-camera video, telemetry, ticketing, VOD, and DVR playback. Custom in-car hardware with the Red5 Linux SDK streams video and data in lockstep, improving judging accuracy and enabling in-race polls and faster betting. Fans enjoy sub-250 ms streams across broadcast, trackside, and in-car views, helping drive 14,000 organic app installs in two months, new betting revenue, and stable multi-event streaming with autoscaling on AWS.
Soundwhale • Global Creative Audio Collaboration

Real-time music collaboration software.
Soundwhale rebuilt its real-time delivery using Red5 Pro and an OCI backbone, then shipped a custom WebRTC client for high-quality, low-delay audio. A lightweight test app from Red5 simplified cross-region debugging and tuning. The result is sub-250 ms, lossless-quality audio even between Tokyo, Mumbai, and California, so artists and engineers collaborate as if they are in the same room.
U.S. Auction Platform • Live Bidding at Scale

Real-time auction software.
Red5 Pro clustering on Amazon EC2 with Stream Manager handled orchestration and autoscaling for the U.S. auction platform, while all streams recorded to Amazon S3 for on-demand playback. Datadog integration improved observability and uptime. Outcomes included sub-250 ms audio and video for fair bidding, a 25% lift in remote participation, up to 40% fewer support requests, longer bidder sessions, and an estimated 20% reduction in infrastructure costs over time.
Vixi Suite • Fan Engagement at Live Events

Real-time fan engagement solution for live events.
The Famous Group uses Red5 Pro to power real-time, interactive stadium and remote experiences with their solution Vixi Suite. They achieved sub-250 ms streaming so in-venue fans can participate instantly, doubled output resolution for tens of thousands of concurrent viewers, and cut EC2 usage by 50% by removing the gateway tier and using a single media server per stream. Co-selling with Red5 also opened new market opportunities.
Conclusion
Ultra-low latency is a critical component of the modern digital landscape, enabling real-time engagement that is transforming the way we live, work, and play. From live sports and betting to traffic monitoring and emergency response, the applications using ultra-low latency streaming are vast and far-reaching.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that ultra-low latency streaming will only become more important, as the demand for real-time, interactive experiences continues to grow. With our commitment to innovation and excellence, we at Red5 will continue delivering ultra-low latency solutions that transform industries and enhance experiences for our users around the world.
FAQs
Does ultra-low latency for live streaming have other names?
Yes. Common terms include sub-second streaming, real-time streaming, interactive live streaming, and ULL streaming.
What is the difference between low latency and ultra low latency?
There is no universal standard. As a rule of thumb, low latency is about 1–3 seconds. Ultra-low latency targets under 1 second, often 250–500 milliseconds for interactive use.
What’s the difference between ultra low and standard latency?
Standard latency for traditional HLS or DASH is often 15–30 seconds or more. Ultra-low latency aims for under 1 second to support real-time interaction, synchronized data, and rapid user feedback.
What is an ultra-low latency network?
A network tuned to minimize delay and jitter using short paths, smart peering, QoS, edge compute, UDP-first transport, and efficient congestion control. The goal is consistent, predictable delivery with minimal buffering.
What is ultra-low latency mode?
Is ultra-low latency important?
Yes for interactive scenarios like betting, auctions, sports watch parties, conferencing, telesurgery training, and remote control.
How is ultra-low latency measured?
Use end-to-end glass-to-glass tests from camera capture to screen display. Timestamp overlays or synchronized clocks help. For two-way apps, also track round-trip media time and jitter to judge interactivity.
What is the lowest latency realistically achievable today?
In practice, well-tuned real-time stacks can reach about 50–250 milliseconds on local or well-peered networks. Physics and network conditions prevent true zero. Global paths typically land a bit higher.
How is ultra-low latency different from negative latency?
Ultra-low latency is real, measurable delay under one second. Negative latency is a marketing term or refers to prediction techniques that mask delay. Actual transmission cannot be less than zero.
What video streaming protocol should I use for archieve ultra-low latency?
WebRTC is currently the best option because it delivers real-time streaming with delays under a second. SRT is another solid choice for reliable, low-latency transport over unpredictable networks. For simpler setup, WHIP and WHEP extend WebRTC over HTTP, streamlining ingest and playback. You can learn more about WHIP vs WHEP in this blog. The upcoming MOQ protocol is expected to support ultra-low-latency streaming once it’s released, expanding these capabilities further.
Product marketing manager with experience at software companies, startups, and enterprises in the live streaming industry since 2018. Her core expertise is SEO, but she also collaborates closely with the product development team to integrate marketing into Red5 solutions and drive adoption. She supports growth through go-to-market strategies, release announcements, email campaigns, case studies, sales enablement materials, social media, and other channels.

